Stent FEA (Crimping, Fatigue, Expand)
A good stent must pass at least these subsequent tests in compliance with international standards (ASTM) for numerical proof (validation) to be successfully completed.
- Stent crimping
- Stent manufacture process (stent expand step by step under thermal conditions)
- Stent fatigue
- Stent foreshortening
- Stent Flexibility test
The following international standards and regulations are used in this context:
ISO 25539-1: Cardiovascular implants – Endovascular devices – Part 1: Endovascular prostheses
ISO 25539-2: Cardiovascular implants – Endovascular devices – Part 2: Vascular stents
ISO 25539-3: Cardiovascular implants – Endovascular devices – Part 3: Vena cava filters
ASTM F2514: Finite Element Analysis (FEA) of Metallic Vascular Stents Subjected to Uniform Radial Loading
ASTM F2477: Standard Test Methods for in vitro Pulsatile Durability Testing of Vascular Stents
ASTM F2942: Standard Guide for in vitro Axial, Bending, and Torsional Durability Testing of Vascular Stents
ASTM F3067: Guide for Radial Loading of Balloon Expandable and Self Expanding Vascular Stents
ASTM F2079: Elastic Recoil of Balloon-Expandable Stents
ASTM F3211: Fatigue-to-Fracture (FtF) Methodology for Cardiovascular Medical Devices.
FDA Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff: Non-Clinical Engineering Tests and Recommended Labeling for Intravascular Stents and Associated Delivery Systems. April 18, 2010
FDA Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff: Reporting of Computational Modeling Studies in Medical Device Submissions. September 21, 2016
Heart Valves:
ISO 5840-3: Cardiovascular implants – Cardiac valve prostheses – Part 3: Heart valve substitutes implanted by transcatheter techniques
ISO 5910: Cardiovascular implants and extracorporeal systems – Cardiac valve repair devices
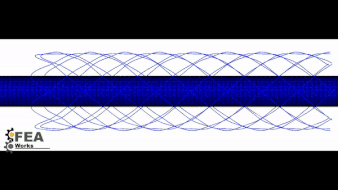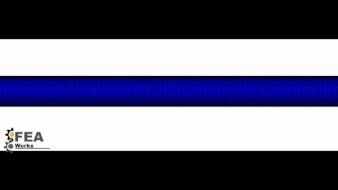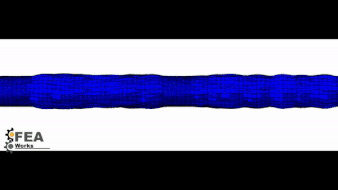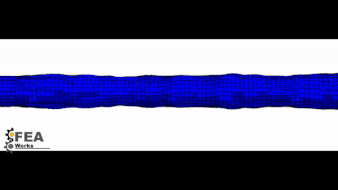
Crimping
Before the stent is loaded in the catheter, it should be crimped before numerically.
The numerical simulation not only helps to select the appropriate stent catheter but also information about the loading of the stent in this position.
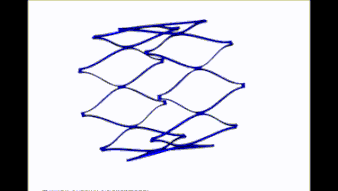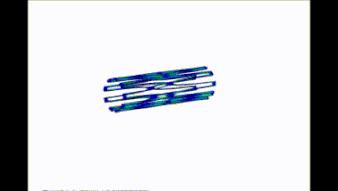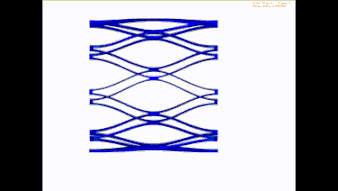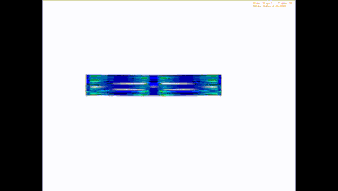
Expand
During stent production, the laser-cut stent is to drive through various heat treatment processes. The expansion calculation represents the processes.
We are happy to advise you on the following points:
- Heat treatment processes of nitinol stents
- Temperature selection with gradual expansion
- Number of heat treatment steps (accompanying the simulation) Depending on the stent diameter

fatigue
The stent must endure at least one million cycles in the human body (depends on the type of stent. We have Fatigue Table of the most used stents).
We have nitinol fatigue parameters and many other stent materials.
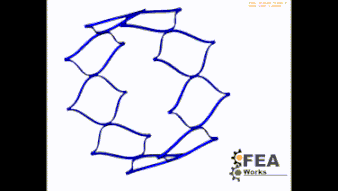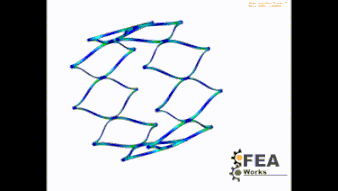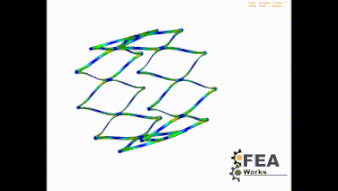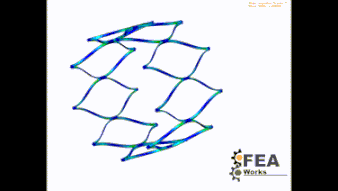
Stent Foreschortening
This test is therefore important and provides information about the compression behavior of the stent when released in man. Which strain (plastic strain) occurs in the stent? could one live with it when the stent experiences these strains?
Stent flexibility test
How flexible is my stent? Can the stent be pushed through a 90 ° bent vessel? This test is therefore important to know where the borders of our stent lie.
